Content
To calculate days payable outstanding, the company’s total amount of accounts payable are divided by the cost of sales during the same specified given time period. It’s fairly obvious that a company must be able to make its payments to those who provide it with services, but paying off those accounts too quickly is actually counterproductive. The longer a company takes to make those payments, the longer the money that is eventually used to make the payments can accrue interest.
If they can afford to purchase goods or services on credit, they will most likely do it, reasonably. Because the money that otherwise used to pay these services or goods can be used for something else, like increasing their capital. By doing this, they increase the value of accounts payable—the variable representing companies’ short-term liabilities to suppliers.
Understanding The Cash Conversion Cycle
A high DPO, however, may also be a red flag indicating an inability to pay its bills on time. The ratio is typically calculated on a quarterly or annual basis, and it indicates how well the company’s cash outflows are being managed. Days Payable Outstanding is an efficiency ratio indicating the average number of days a company takes to pay its bills and invoices.
Some companies calculate DPO using the accounts payable balance at the end of the relevant period, while others may use the average account payable balance during the relevant period. Because of these cost savings advantages, companies with supplier contracts similar to this have lower DPOs.
Working capital management and performance of SME sector, Gul, S., Khan, M. B., Raheman, S. U., Khan, M. T., Khan, M., & Khan, W. GrowthForce accounting services provided through an alliance with SK CPA, PLLC. Finally, a high DPO could indicate that the company is doing an excellent job managing its working capital. It’s essential to understand and optimize all of your AP operations by taking the time to calculate DPO.
Related To Days Payable Outstanding
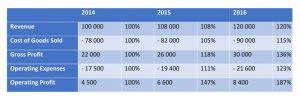
Since bills should be paid on their due date, a good DPO should be just less than the average payment terms offered by vendors. DPO and the average number of days it takes a company to pay its bills are important concepts in [financial modeling. When calculating a company’s free cash flow to the firm , changes Days Payable Outstanding in net working capital impact cash flow, and, thus, the average number of days they take to pay bills can have an impact on valuation . From this result, we can estimate that, on average, it takes 48.67 days for the company to pay off each of its accounts payable to its vendors and/or suppliers.
It is therefore only beneficial to compare DPO with other companies in the same sector – there is no concrete number that represents a ‘good’ or ‘bad’ DPO. It can be beneficial to compare a company’s DPO to the average DPO within its industry. A higher or lower than average DPO may indicate a few different things. It’s important to keep all of these things in mind when analyzing the days outstanding payable ratio. Ultimately, the DPO may depend on the contract between the vendor and the company. In that case, the company will have to weigh the option of holding on the cash versus availing the discount. 3) Competitiveness – if there are many suppliers with little differentiation than they will have to offer longer payment cycle to gain business from a client.
What Is days Payable Outstanding?
In addition, the company’s COGS is anticipated to grow 10% year-over-year through the entire projection period. Free Financial Modeling Guide A Complete Guide to Financial Modeling This resource is designed to be the best free guide to financial modeling! Similar calculations can be used for technology leader Microsoft , which had $2.8 billion as AP and $41.3 billion as COGS, leading to a DPO value of 24.7 days. In another version, the average value of beginning AP and ending AP is taken, and the resulting figure represents the DPO value during that particular period. Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance.
- It can also give rise to the risk of supply chain disruption if cash-strapped suppliers struggle to fulfil orders.
- The company is taking more number of days to pay back to its suppliers.
- The amount outstanding towards the suppliers from whom goods/services have been procured on credit is recorded as Accounts Payable.
- However, it can also indicate that a company has more cash to use for shorter investments, like a government bond, which shows a positive financial status.
- It may be helpful to measure a company’s DPO against the average value number of its industry, as this ratio can indicate a company’s financial status overall.
- You can increase payable days by paying your suppliers on or near due dates, but not any sooner.
- When comparing DPO between companies, it’s important to remember that practices can vary considerably between different industry sectors and geographical locations.
In order to calculate https://www.bookstime.com/, you first need to determine a company’s average payable period. This is calculated by dividing the total amount of days it took the company to pay its bills by the total amount of days in the period. The result is then multiplied by 365 to get the average number of days.
How Does Days Payable Outstanding Work?
As this is the case, days payable outstanding becomes an important metric to determine the financial strength of a business. A high DPO indicates the company takes a longer period of time for making payments to its trade creditors. A company acquires raw materials and services from its suppliers and vendors on a credit basis.

Regularly measuring your company’s performance is essential to improving it. And in accounts payable , one of the most effective metrics for tracking your overall efficiency and productivity is days payable outstanding, or DPO. It’s not complicated or difficult, but it can provide you with some valuable insights into your process efficiency and cash cycle. Where ending A/P is the accounts payable balance at the end of the accounting period being considered and Purchase/day is calculated by dividing the total cost of goods sold per year by 365 days. Days Payable Outstanding measures the number of days a company takes on average before paying outstanding supplier/vendor invoices for purchases made on credit. Days Payable Outstanding is how long it takes, on average, for a company to pay its suppliers. Accounts Receivable Days is how long it takes, on average, for the company to be paid back by its customers.
Days Payable Outstanding Dpo Calculation With Steps
Learn more about financial ratios and how they help you understand financial statements. In other words, it takes this company an average of about 60 days to pay their bills. This lengthy time span may be good for working capital but not good for supplier relationships. Days payable outstanding , defined also as days purchase outstanding, indicates how many days on average a company pay off itsaccounts payables during an accounting period. A high days payable outstanding is generally considered a good thing.
- To learn a company’s DPO, divide your previously multiplied sum by the amount you calculated for the COGS.
- Otherwise, the term of the loan may not be as favorable as it used to, not to mention the companies can pay less if they pay off its debts earlier.
- In another version, the average value of beginning AP and ending AP is taken, and the resulting figure represents the DPO value during that particular period.
- By doing this, they increase the value of accounts payable—the variable representing companies’ short-term liabilities to suppliers.
- By taking a strategic approach, you can free up working capital to fuel your business’s growth, strengthen corporate cost management, and reduce the complexity in accounts payable processing.
Imagine if a company allows a 90-day period for its customers to pay for the goods they purchase but has only a 30-day window to pay its suppliers and vendors. This mismatch will result in the company being prone to cash crunch frequently. Conversely, a reduction in your firm’s DSO and an increase in DPO will lead to improved cash flow for your business. High DSO indicates a company takes longer to receive cash from customers and is indicative of loose credit policy. Loose credit policy may prevent the company from reinvesting in the business as it spends more time waiting for payments.
Reports You Need To Compute Your Days Payable Outstanding
To calculate the DPO you divide the ending accounts payable by the annual cost of goods sold per day. An easier way to manage both your cash conversion cycle and your cash flow with ease, ensuring everyone is paid on time while you have all the cash on hand you need to drive innovation and expansion. In general, high DPOs are looked at favorably; it indicates that the firm is able to use cash to other uses for an extended period of time. Extremely high DPOs potentially highlight liquidity issues OR extensive credit terms that favor the company . Let’s say a company has an accounts payable balance of $30mm in 2020 and COGS of $100mm in the same period. Days payable outstanding computes the average number of days a company needs to pay its bills and obligations.
Considerations When Calculating Accounts Payable Days
The accounts payable line item represents the accumulated balance of unmet payments for past purchases made by the company. There is no clear-cut number on what constitutes a healthy days payable outstanding, as the DPO varies significantly by industry, competitive positioning of the company, and its bargaining power. With such a significant market share, the retailer can negotiate deals with suppliers that heavily favor them. Two different versions of the DPO formula are used depending upon the accounting practices.
Now, imagine that it’s not a person that purchases the electricity in a loan, but a company. Additionally, on the balance sheet, accounts payable falls under the current liabilities section. Keep in mind the word ‘current’ so any long-term liabilities are not included. The number of days – quite obvious – is what the cost of sales and the account payable are based on. Lastly, the accounts payable represent the amount of money that’s being owed to the supplier or vendor of a certain company. A company’s DPO can be found out by firstly dividing the cost of sales by the number of days and then taking the accounts payable and dividing them by the result of the first calculus.
Before calculating days payable outstanding, you need accounts payable to your suppliers at the end of the current and prior year. Notice that accounts payable at the end of the prior year is the beginning balances for the current year. You can use the days payable outstanding calculator below to quickly evaluate the average days it takes for a company to pay its payable outstanding to its suppliers by entering the required numbers. It is often determined as 365 for yearly calculation or 90 for quarterly calculation. By multiplying the result of the calculation with the number of days, we can determine the average days needed for companies to pay off their payable outstanding to its vendors .
